What is Inter-VLAN Routing?
VLANs are used to segment switched Layer 2 networks for a variety of reasons. Regardless of the reason, hosts in one VLAN cannot communicate with hosts in another VLAN unless there is a router or a Layer 3 switch to provide routing services.
Inter-VLAN routing is the process of forwarding network traffic from one VLAN to another VLAN.
There are three inter-VLAN routing options:
- Legacy Inter-VLAN routing– This is a legacy solution. It does not scale well.
- Router-on-a-Stick– This is an acceptable solution for a small to medium-sized network.
- Layer 3 switch using switched virtual interfaces (SVIs)– This is the most scalable solution for medium to large organizations
Legacy Inter-VLAN Routing
- The first inter-VLAN routing solution relied on using a router with multiple Ethernet interfaces. Each router interface was connected to a switch port in different VLANs. The router interfaces served as the default gateways to the local hosts on the VLAN subnet.
- Legacy inter-VLAN routing using physical interfaces works, but it has a significant limitation. It is not reasonably scalable because routers have a limited number of physical interfaces. Requiring one physical router interface per VLAN quickly exhausts the physical interface capacity of a router.
- Note: This method of inter-VLAN routing is no longer implemented in switched networks and is included for explanation purposes only.

Router-on-a-Stick Inter-VLAN Routing
The ‘router-on-a-stick’ inter-VLAN routing method overcomes the limitation of the legacy inter-VLAN routing method. It only requires one physical Ethernet interface to route traffic between multiple VLANs on a network.
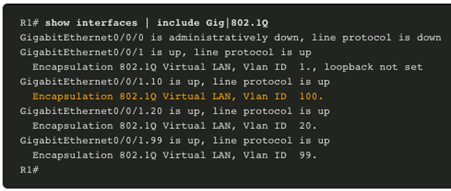
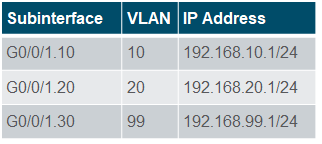
- A Cisco IOS router Ethernet interface is configured as an 802.1Q trunk and connected to a trunk port on a Layer 2 switch. Specifically, the router interface is configured using subinterfaces to identify routable VLANs.
- The configured subinterfaces are software-based virtual interfaces. Each is associated with a single physical Ethernet interface. Subinterfaces are configured in software on a router. Each subinterface is independently configured with an IP address and VLAN assignment. Subinterfaces are configured for different subnets that correspond to their VLAN assignment. This facilitates logical routing.
- When VLAN-tagged traffic enters the router interface, it is forwarded to the VLAN subinterface. After a routing decision is made based on the destination IP network address, the router determines the exit interface for the traffic. If the exit interface is configured as an 802.1q subinterface, the data frames are VLAN-tagged with the new VLAN and sent back out the physical interface
Note: The router-on-a-stick method of inter-VLAN routing does not scale beyond 50 VLANs.
Inter-VLAN Routing on a Layer 3 Switch
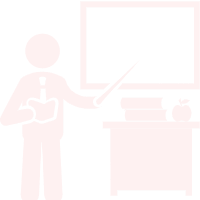
The modern method of performing inter-VLAN routing is to use Layer 3 switches and switched virtual interfaces (SVI). An SVI is a virtual interface that is configured on a Layer 3 switch, as shown in the figure.
Note: A Layer 3 switch is also called a multilayer switch as it operates at Layer 2 and Layer 3. However, in this course we use the term Layer 3 switch
Inter-VLAN Routing on a Layer 3 advantages
The following are advantages of using Layer 3 switches for inter-VLAN routing:
- They are much faster than router-on-a-stick because everything is hardware switched and routed.
- There is no need for external links from the switch to the router for routing.
- They are not limited to one link because Layer 2 EtherChannels can be used as trunk links between the switches to increase bandwidth.
- Latency is much lower because data does not need to leave the switch in order to be routed to a different network.
- They more commonly deployed in a campus LAN than routers.
- The only disadvantage is that Layer 3 switches are more expensive.
Router-on-a-Stick Scenario
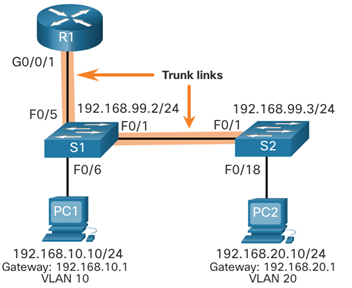

Routing Scenario on a Layer 3 Switch
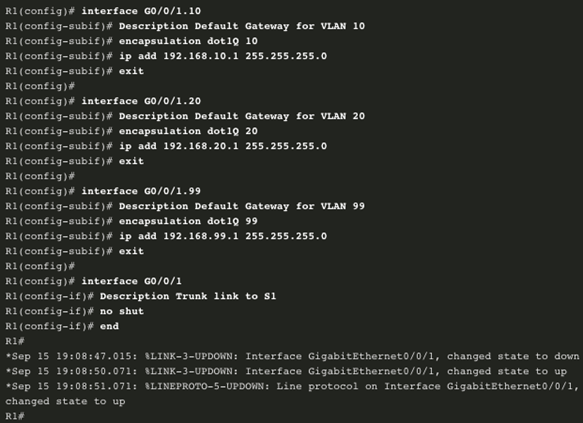
Complete the following steps to configure D1 to route with R1:
- Step 1. Configure the routed port. Use the no switchport command to convert the port to a routed port, then assign an IP address and subnet mask. Enable the port.
- Step 2. Enable routing. Use the ip routing global configuration command to enable routing.
- Step 3. Configure routing. Use an appropriate routing method. In this example, Single-Area OSPFv2 is configured
- Step 4. Verify routing. Use the show ip route command.
- Step 5. Verify connectivity. Use the ping command to verify reachability.

Common Inter-VLAN Issues
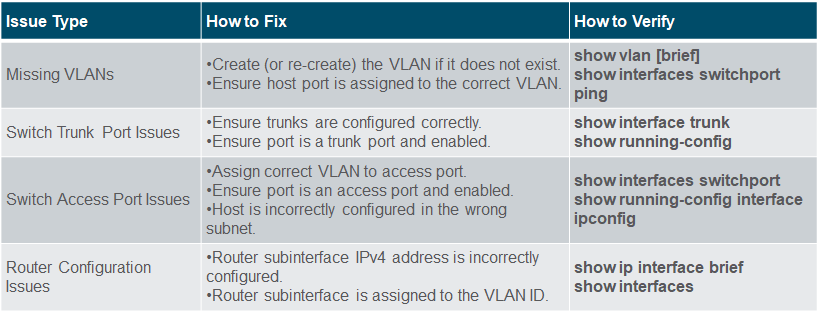
Troubleshoot Inter-VLAN Routing Scenario